字典树
概念
概念
字典树是一种按照字符串的前缀构建的一种特殊数据结构,是一种字典的存储结构,每个“单词”从根节点出发一直到某一节点为止的路径(通过节点上的bool end来判断是否为单词结尾),路径上的字母连起来即是所存储的“单词”。
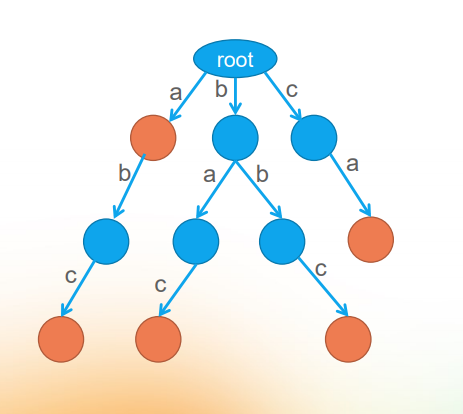
功能
- 维护字典树(即插入“单词”)
- 查询字典树中是否存在某一完整字符串
- 统计字符串出现次数
- 字典序排序
- 求集合内字符串之间的公共前缀
实现
- 设计
力扣相关:208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
剑指 Offer II 062. 实现前缀树
- 结构体定义
typedef struct Trie {
bool end; //用来记录从根节点到当前节点的路径是否为一个完整字符串
struct Trie *next[26]; //普通字符串只有26种字符
} Trie;- 创建节点
Trie* trieCreate() {
struct Trie *node = (struct Trie *)malloc(sizeof(Trie));
node->end = false;
memset(node->next, 0, sizeof(node->next));
return node;
}c++中以上两个操作可以直接进行合并,定义一个
Trie类,然后创建节点即为Trie类的构造函数.
- 插入操作
void trieInsert(Trie* obj, char * word) {
int n = strlen(word);
Trie *cur = obj;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int childptr = word[i] - 'a'; //将字符映射到整型
if(cur->next[childptr] == NULL){ //为null说明字典树中没有该单词
cur->next[childptr] = trieCreate();
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];
}
cur->end = 1; //单词插入完成,将当前节点的end置true来表示为单词末尾
}- 查询字典中是否存在某个完整字符串
bool trieSearch(Trie* obj, char * word) {
int n = strlen(word);
Trie *cur = obj;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int childptr = word[i] - 'a';
if(cur->next[childptr] == NULL){ //为null说明当前的单词不存在于字典树中,返回false
return false;
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];
}
return cur->end; //如果字典树中存在路径与单词相重合,直接判断当前节点是否为true
}- 查询字典中是否存在某个字符串前缀
bool trieStartsWith(Trie* obj, char * prefix) {
int n = strlen(prefix);
Trie *cur = obj;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int childptr = prefix[i] - 'a';
if(cur->next[childptr] == NULL){
return false;
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];
}
return true; //与完整字符串不同的地方是不需要看当前节点是不是单词的末尾
}- 应用
-
在英语中,我们有一个叫做
词根(root) 的概念,可以词根后面添加其他一些词组成另一个较长的单词——我们称这个词为继承词(successor)。例如,词根an,跟随着单词other(其他),可以形成新的单词another(另一个)。现在,给定一个由许多词根组成的词典
dictionary和一个用空格分隔单词形成的句子sentence。你需要将句子中的所有继承词用词根替换掉。如果继承词有许多可以形成它的词根,则用最短的词根替换它。你需要输出替换之后的句子。
示例1:
输入:dictionary = [“cat”,”bat”,”rat”], sentence = “the cattle was rattled by the battery”
输出:”the cat was rat by the bat”示例2:
输入*:dictionary = [“a”,”b”,”c”], sentence = “aadsfasf absbs bbab cadsfafs”
输出:”a a b c”- 思路:将
dictionary中的词根存入到一个字典树中,并在字典树中依次查找sentence的每个单词并返回对应的前缀,如果不存在相应的前缀则返回原来的单词,并将结果存在答案res中即可。
- 思路:将
class Tries {
public:
bool end;
Tries *next[26];
Tries(){
end = false;
memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
}
void Insert(Tries *obj, string word){
int n = word.length();
Tries *cur = obj;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int childptr = word[i] - 'a';
if(cur->next[childptr] == NULL){
cur->next[childptr] = new(Tries);
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];
}
cur->end = true;
}
string findPredix(Tries *obj, const string& word){
string Predix;
Tries *cur = obj;
for(char ch: word){
int childptr = ch - 'a';
if(cur->next[childptr] != NULL){
if(cur->end == true) break;
Predix += ch;
}else{
break;
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];
}
return cur->end == true ? Predix : word;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
string replaceWords(vector<string>& dictionary, string sentence) {
string res;
Tries *root = new(Tries);
for(string str: dictionary){
root->Insert(root, str);
}
string tmpStr;
for(int i = 0; i < sentence.length(); i++){
char ch = sentence[i];
if(ch != ' '){
tmpStr += ch;
}else{
string str = root->findPredix(root, tmpStr);
res += str + " ";
tmpStr = "";
}
}
res += root->findPredix(root, tmpStr);
return res;
}
};- 421. 数组中两个数的最大异或值
-
给定一个整数数组
nums,返回nums[i] XOR nums[j]的最大运算结果,其中0 ≤ i ≤ j < n。示例1:
输入:nums = [3,10,5,25,2,8]
输出:28示例2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:0示例3:
输入:nums = [2,4]
输出:6示例4:
输入:nums = [8,10,2]
输出:10示例5:
输入:nums = [14,70,53,83,49,91,36,80,92,51,66,70]
输出:127- 思路:将每个数转换为二进制字符串并按由高位到低位建立字典树(不能由低到高,因为字典树中树的左右子树的深度未知,需要遍历整个树才能得到答案,基本上就是$O(n^2)$的复杂度了;而由高到低,我们只需要按照有相反的路径就走相反的路径、没有就走相同的路径,尽可能往深的走,那么就一定能得到答案),然后对数组进行遍历,即可得到答案。这道题属于01字典树,经典题目。
class Tries {
public:
Tries *next[2];
Tries(){
memset(next, 0, sizeof(next));
}
void insert(Tries *obj, string tmpStr){
Tries *cur = obj;
for(char ch: tmpStr){
int childptr = ch - '0';
if(cur->next[childptr] == NULL){
cur->next[childptr] = new(Tries);
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];
}
}
int search(Tries *obj, string tmpStr){
Tries *cur = obj;
int res = 0;
for(char ch: tmpStr){
//代码优化版,性能并没有优化
/*int childptr = (ch - '0') ^ 1; //取相反数,0取1,1取0
if(cur->next[childptr]){
res = 2*res + 1;
}else{
childptr ^= 1;
res = 2*res;
}
cur = cur->next[childptr];*/
int childptr = (ch - '0');
if(childptr){ //当前位为1
if(cur->next[0]){ //相反位不为null
cur = cur->next[0]; //则往相反位走
res = 2*res + 1; //加上当前位1
}else{
cur = cur->next[1]; //相反位为null,走同位
res = 2*res; //当前位相同,不加1
}
}else{ //当前位为0
if(cur->next[1]){ //相反位不为null
cur = cur->next[1]; //则往相反位走
res = 2*res + 1; //加上当前位1
}else{
cur = cur->next[0]; //相反位为null,走同位
res = 2*res; //当前位相同,不加1
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int findMaximumXOR(vector<int>& nums) {
Tries *root = new(Tries);
int ans = 0;
string s = "";
for(int num: nums){ //构建01字典树
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; --i){ //数转二进制字符串,题目中num<2^31-1,所以最多是30位
s += ('0' + ((num>>i) & 1));
}
root->insert(root, s); //插入字典树
s = ""; //清空中间字符串
}
for(int num: nums){
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; --i){
s += ('0' + ((num>>i) & 1));//数转二进制字符串
}
ans = max(ans, root->search(root, s));
s = ""; //清空中间字符串
}
return ans;
}
};
