- 27. 移除元素
- 344. 反转字符串
- 剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
- 151.翻转字符串里的单词
- 206.反转链表
- 19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
- 142.环形链表II
- 15. 三数之和
- 18. 四数之和
- 总结
1 移除元素
- 题目链接:27. 移除元素
1.1 题目描述
给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要 原地 移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并 原地 修改输入数组。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例1:
输入: nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3
输出: 2, nums = [2,2]
示例2:
输入: nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2
输出: 5, nums = [0,1,4,0,3]
1.2 思路
设置两个指针,首先判断快指针对应的数组中的值是否等于 val, 如果是则不进行操作,如果不等于则说明这个当前遍历到的元素应该进行保留,因而将其赋给慢指针指向的位置。整体的思路就是遍历一遍数组,遇到与 val 不一样的元素就把该元素插到原数组的前端(用慢指针指定位置),最后返回慢指针即为答案。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int fast = 0, slow = 0;
for(; fast < nums.size(); ++fast){
if(nums[fast] == val){
continue;
}
nums[slow++] = nums[fast];
}
return slow;
}
};C实现
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
int order=0;
for(int i=0;i<numsSize;i++){
if(nums[i]!=val){
nums[order++]=nums[i];
}
}
return order;
} 2 反转字符串
- 题目链接:344. 反转字符串
2.1 题目描述
编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 s 的形式给出。
不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组、使用 O(1) 的额外空间解决这一问题。
示例1:
输入: s = [“h”,”e”,”l”,”l”,”o”]
输出: [“o”,”l”,”l”,”e”,”h”]
示例2:
输入: s = [“H”,”a”,”n”,”n”,”a”,”h”]
输出: [“h”,”a”,”n”,”n”,”a”,”H”]
2.2 思路
设置两个指针,分别指向vector的头和尾,然后两两进行交换,交换完成则头指针后移、尾指针前移直至二者相遇。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector<char>& s) {
int l = 0, r = s.size()-1;
while(l < r){
char ch = s[l];
s[l++] = s[r];
s[r--] = ch;
}
}
};C实现
void reverseString(char* s, int sSize){
if(sSize<=1){
return s;
}
int left=0,right=sSize-1;
while(left<right){
s[left]=s[left]^s[right];
s[right]=s[left]^s[right];
s[left]=s[left]^s[right];
left++;right--;
}
return s;
} 3 替换空格
- 题目链接:剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
3.1 题目描述
请实现一个函数,把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成”%20”。
示例1:
输入: s = “We are happy.”
输出: “We%20are%20happy.”
3.2 思路
遍历s,当当前字符不为空格时直接将当前字符加到答案res后边,否则则在res后边加上"%20"即可。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
string res;
int ptr = 0;
for(char ch: s){
if(ch != ' '){
res += ch;
}else{
res += "%20";
}
}
return res;
}
};C实现
char* replaceSpace(char* s){
char *res = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char)*(3*strlen(s)+1));
int index = 0;
char tmpChar[4] = "%20";
for(int i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++){
if(s[i] != ' '){
res[index++] = s[i];
}else{
res[index++] = '%';
res[index++] = '2';
res[index++] = '0';
//strcat(res, tmpChar);
//index += 3;
}
}
res[index] = '\0';
return res;
}
C实现中记得最后在答案res的末端加上空字符\0, 否则报错.
4 颠倒字符串中的单词
- 题目链接:151. 颠倒字符串中的单词
4.1 题目描述
给你一个字符串 s ,颠倒字符串中 单词 的顺序。
单词 是由非空格字符组成的字符串。s 中使用至少一个空格将字符串中的 单词 分隔开。
返回 单词 顺序颠倒且 单词 之间用单个空格连接的结果字符串。
注意:输入字符串 s 中可能会存在前导空格、尾随空格或者单词间的多个空格。返回的结果字符串中,单词间应当仅用单个空格分隔,且不包含任何额外的空格。
示例1:
输入: s = “the sky is blue”
输出: “blue is sky the”
示例2:
输入: s = “ hello world “
输出: “world hello”
示例3:
输入: s = “a good example”
输出: “example good a”
4.2 思路
先将s 的头尾多余的空格去掉,然后遍历s并将当前的字符插入到res中,注意,当单词间出现多余的空格直接continue。遍历完成后,将res翻转,然后遍历res,一遇到空格就将当前的单词翻转。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
void reverse(string& s, int l, int r){
while(l < r){
char ch = s[l];
s[l] = s[r];
s[r] = ch;
++l, --r;
}
}
string reverseWords(string s) {
int l = 0, r = s.length() - 1;
while(s[r] == ' '){
--r;
}
while(s[l] == ' '){
++l;
}
string res;
for(int i = l; i <= r; ++i){
if((res.length() && res.back() != ' ') || s[i] != ' '){
res.push_back(s[i]);
}
}
reverse(res, 0, res.length()-1);
l = 0, r= 0;
for(; r < res.length(); r++){
if(res[r] != ' '){
continue;
}
reverse(res, l, r-1);
l = r + 1;
}
reverse(res, l, r-1);
return res;
}
};C实现
char* reverse(char* s, int left, int right){
while(left < right){
s[left] = s[left]^s[right];
s[right] = s[left]^s[right];
s[left] = s[left]^s[right];
left++;
right--;
}
return s;
}
char * reverseWords(char * s){
int slow = 0, fast = 0;
while(s[fast]==' ') fast++;
for(; fast<strlen(s)-1; fast++){ //处理前后、单词间多余的空格
if(s[fast] == ' ' && s[fast+1] ==' '){
continue;
}else{
s[slow++] = s[fast];
}
}
if(s[fast]==' '){
s[slow] = '\0';
}else{
s[slow++] = s[fast];
s[slow] = '\0';
}
reverse(s, 0, slow-1);
int left = 0, right = 0;
while(right < slow){
while(right < slow&&s[right] != ' ') right++;
reverse(s, left, right-1);
right += 1;
left = right;
}
return s;
} 5 反转链表
- 题目链接:206. 反转链表
5.1 题目描述
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例1:
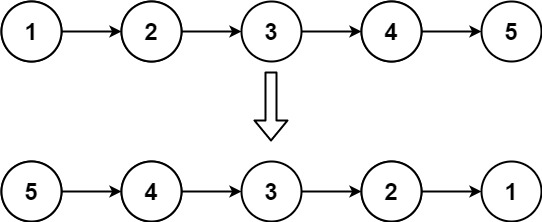
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [5,4,3,2,1]
示例2:
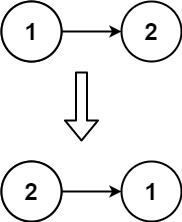
输入: head = [1,2]
输出: [2,1]
示例3:
输入: head = []
输出: []
5.2 思路
添加一个虚拟节点 pre 并置为 nullptr ,用 cur 遍历原链表,每次将 cur 的 next 指向 pre, 然后将 cur 和 prev 后移一位。由于 cur 后移前其 next 指向已经改变,即指向了上一个节点,因而我们无法通过 cur->next 来访问原链表中 cur 的下一个节点,因而在修改 cur 的 next 指向前将 cur->next 存起来。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
struct ListNode* pre = nullptr, *cur = head;
while(cur){
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};C实现
//递归版
/*struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL||head->next == NULL){
return head;
}
struct ListNode* newHead;
newHead = reverseList(head->next); //newHead是最后一层的return,这里赋给倒数第二层的newhead
head->next->next = head; //然后倒数第二次return那个newhead,一直循环不变
head->next = NULL;
return newHead; //所以这里return的其实就是最后一层的head
}*/
//迭代版
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* pre = NULL;
while(cur){
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
} 6 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 题目链接:19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
6.1 题目描述
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例1:
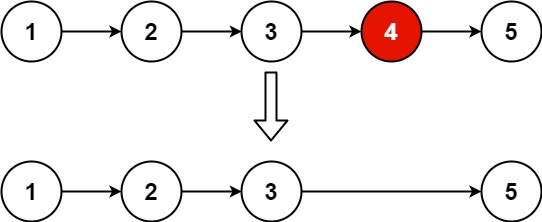
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出: [1,2,3,5]
示例2:
输入: head = [1], n = 1
输出: []
示例3:
输入: head = [1,2], n = 1
输出: [1]
6.2 思路
双指针典型题目。快指针先向后移动 n 步,然后快慢指针同步向后移动,当快指针的 next 指向 nullptr 时,慢指针的 next 恰好指向倒数第 n 个节点,然后直接slow->next = slow->next->next,即将慢指针的 next 指向下下个节点。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* fast = head, *slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
if(n){
--n;
}else{
slow = slow->next;
}
fast = fast->next;
}
if(n){
head = head->next;
}else{
slow->next = slow->next->next;
}
return head;
}
};C实现
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n){
if(head->next == NULL) return NULL;
struct ListNode *left = head;
struct ListNode *right = head;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
right = right->next;
}
if(right==NULL){
return head->next;
}
while(right!=NULL&&right->next!=NULL){
right=right->next;
left=left->next;
}
left->next = left->next->next;
return head;
} 7 链表相交
- 题目链接:面试题 02.07. 链表相交
7.1 题目描述
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
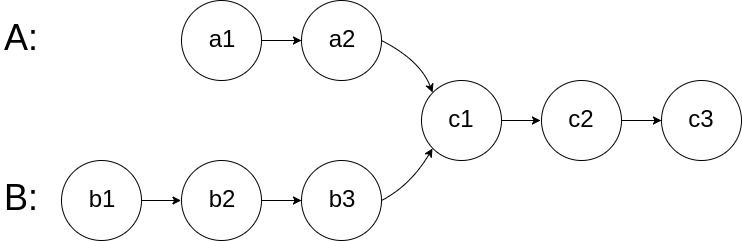
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例1:
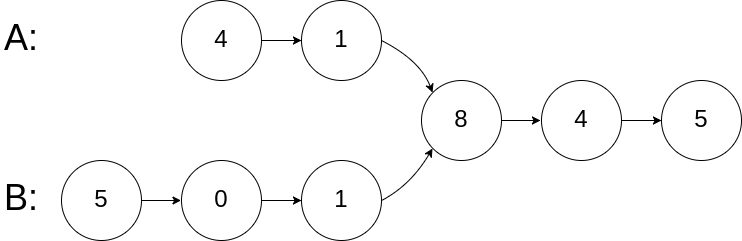
输入: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出: Intersected at ‘8’
示例2:
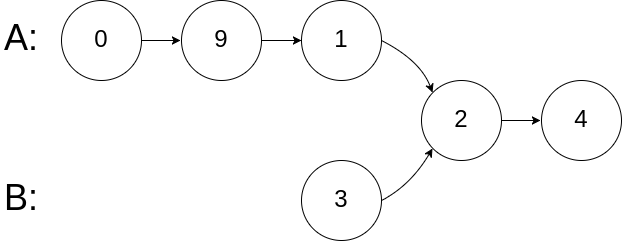
输入: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出: Intersected at ‘2’
示例3:
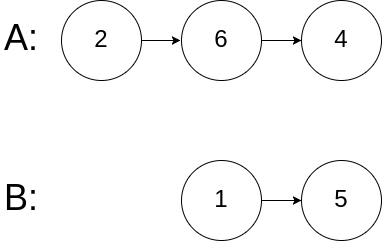
输入: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出: null
7.2 思路
创建两个指针分别遍历两个链表,如果出现 ptr1 == ptr2, 则说明找到交点,而当两个指针指向nullptr, 将其指向另一个链表的表头,如果有交点,那么这样过后就一定会在交点相遇。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *ptrA = headA, *ptrB = headB;
while(ptrA != ptrB){
if(!ptrA){
ptrA = headB;
}else{
ptrA = ptrA->next;
}
if(!ptrB){
ptrB = headA;
}else{
ptrB = ptrB->next;
}
}
return ptrA;
}
};C实现
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
if(headA==NULL||headB==NULL) return NULL;
struct ListNode* pA =headA;
struct ListNode* pB =headB;
while(pA!=pB){
if(pA==NULL){
pA = headB;
}else{
pA = pA->next;
}
if(pB==NULL){
pB = headA;
}else{
pB = pB->next;
}
}
return pA;
} 8 环形链表 II
- 题目链接:142. 环形链表 II
8.1 题目描述
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例1:
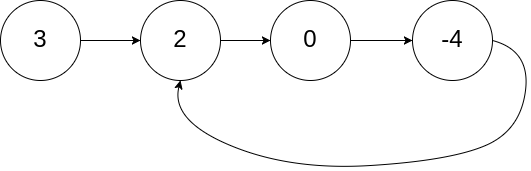
输入: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出: 返回索引为 1 的链表节点
示例2:
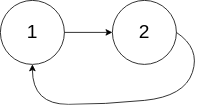
输入: head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出: 返回索引为 0 的链表节点
示例3:

输入: head = [1], pos = -1
输出: 返回 null
8.2 思路
设置两个指针,快指针 fast 每次走两步, 慢指针 slow 每次走一步。
fast 先进入环,slow 需要走 a 步才到达环的入口,此时 fast 已经走了 2a 步。当 slow 到达环入口,设此时 fast 与 slow 之间的距离为 x.
fast 什么时候能追上 slow 实现“套圈”呢?由于 fast 与 slow 间的距离每步缩小 1,那么 slow 走 x 步时 fast 就可以追上 slow . 注意:当 slow 到达环入口时两个指针间的距离x 是必定小于环的长度 (可能为 0 ).即慢指针一圈还没走完就会被快指针追上. 设相遇点距离入环点b,则有(设相遇时快指针已经走了 n 圈)
得:
即
那么想要知道入环点,有一种直接得方法就是让指针自己走到入环点,如何实现?通过上式可以得知,让慢指针走c + (n-1)(b+c), 同时让一个从链表头出发的指针按相同的速度行走,那么必定会在环入口相遇。为什么呢?让慢指针走c + (n-1)(b+c)其实就是走完当前的那一圈,然后再走(n-1)圈,这段距离恰好就是链表头到环入口的距离,所以二者就在环入口相遇。

完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return nullptr;
ListNode* fast = head, *slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast && fast == slow){
fast = head;
while(fast!=slow){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};C实现
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL) return NULL;
struct ListNode *fast=head,*slow=head;
while(1){
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==NULL||fast->next==NULL){
return NULL;
}
fast=fast->next->next;
if(fast==slow){
struct ListNode *ptr = head;
while(ptr!=slow){
slow=slow->next;
ptr=ptr->next;
}
return ptr;
}
}
return NULL;
} 9 三数之和
- 题目链接:15. 三数之和 “15. 三数之和”)
9.1 题目描述
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例1:
输入: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
示例2:
输入: nums = []
输出: []
示例3:
输入: [0]
输出: []
9.2 思路
先将数组进行排序,然后分别用first、second和third分别指代第一、第二和第三个选取的数字的索引,用 first 遍历数组,然后 target 设为 -nums[first](题目要三数之和为 0 ),然后second 赋为 first + 1, 而third 赋为 nums.size()-1,进行循环判断nums[second] + nums[third] 是否等于 target,若是则将三个索引插入答案,并将second和third向中间移动(要移动到不等于上一个值的地方,因为题目规定 不能出现重复的三元组); 若nums[second] + nums[third] 小于 target,则应该试图把第二和第三的加和变大,所以将 second 右移一位;若nums[second] + nums[third] 大于 target,则应该试图把第二和第三的加和变小,所以将 third 左移一位。
这题不大适用哈希表,因为题目规定 不能出现重复的三元组,如果用哈希表的话,插入完成后需要遍历答案进行去重。
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
int n = nums.size();
if(n < 3) return res;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int first = 0; first < n -2; ++first){
if(first && nums[first] == nums[first-1]){
continue;
}
int target = - nums[first];
int second = first + 1, third = n - 1;
while(second < third){
int tmp = nums[second] + nums[third];
if(tmp == target){
res.push_back({nums[first],nums[second],nums[third]});
while(second < third && nums[second] == nums[++second]);
while(second < third && nums[third] == nums[--third]);
}else if(tmp < target){
++second;
}else{
--third;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};C实现
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b){
return (*(int *)a - *(int *)b);
}
int** threeSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
*returnSize = 0;
if(numsSize < 3) return NULL;
int n = numsSize;
int** ret = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *)*n*n);
*returnColumnSizes = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*n*n);
qsort(nums, n, sizeof(int), cmp);
for(int i = 0; i < n-2; i++){
if(nums[i] > 0) return ret;
if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]){
continue;
}
int left= i + 1, right = n-1;
while(left < right){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == 0){
ret[*returnSize] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*3);
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = 3;
ret[*returnSize][0] = nums[i];
ret[*returnSize][1] = nums[left];
ret[*returnSize][2] = nums[right];
(*returnSize)++;
while(left < right && nums[left ] == nums[++left]); //这两行划重点!!!!!!!
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[--right]);
}else if(sum > 0){
right--;
}else{
left++;
}
}
}
return ret;
} 10 四数之和
- 题目链接:18. 四数之和 “18. 四数之和”)
10.1 题目描述
给你一个由 n 个整数组成的数组 nums ,和一个目标值 target 。请你找出并返回满足下述全部条件且不重复的四元组 [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]] (若两个四元组元素一一对应,则认为两个四元组重复):
0 <= a, b, c, d < na、b、c和d互不相同nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案 。
示例1:
输入: nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
输出: [[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
示例2:
输入: nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2]]
10.2 思路
思路和”三数之和”思路一致,只是多加了一层 for 循环即可,时间复杂度为 $O(n^3logn)$
完整代码如下:
Cpp实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
int n = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int first = 0; first < n - 3; ++first){
if(first && nums[first] == nums[first-1]){
continue;
}
for(int second = first+1; second < n-2; ++second){
if(second > first+1 && nums[second] == nums[second-1]){
continue;
}
int rest = target - nums[first] - nums[second];
int third = second + 1, fourth = n - 1;
while(third < fourth){
int tmp = nums[third] + nums[fourth];
if(tmp == rest){
res.push_back({nums[first],nums[second],nums[third],nums[fourth]});
while(third < fourth && nums[third] == nums[++third]);
while(third < fourth && nums[fourth] == nums[--fourth]);
}else if(tmp < rest){
++third;
}else{
--fourth;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};C实现
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b){
return (*(int *)a - *(int *)b);
}
int** fourSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
int n = numsSize;
*returnSize = 0;
if(n < 4) return NULL;
qsort(nums, n, sizeof(int), cmp);
int** ret = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * n* n* n);
*returnColumnSizes = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) *n *n *n);
for(int first = 0; first < n-3; first++){
if(first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first-1]){
continue;
}
for(int second = first + 1; second < n-2; second++){
if(second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second-1]){
continue;
}
int sum = target - nums[first] - nums[second];
int third = second + 1, fourth = n-1;
while(third < fourth){
if(nums[third] + nums[fourth] == sum){
ret[*returnSize] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*4);
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = 4;
ret[*returnSize][0] = nums[first];
ret[*returnSize][1] = nums[second];
ret[*returnSize][2] = nums[third];
ret[*returnSize][3] = nums[fourth];
(*returnSize)++;
while(fourth > third && nums[fourth] == nums[--fourth]);
while(fourth > third && nums[third] == nums[++third]);
}else if(nums[third] + nums[fourth] < sum){
third++;
}else{
fourth--;
}
}
}
}
return ret;
} 总结
404…

