最短路径问题
给定一个起点(和终点),求以该起点为源到其他所有点(终点)的最短路径长度。通常采用BFS对图进行遍历,当第一次走到目标点时,此时BFS的轮数即为起点到当前点的最短距离。其伪代码如下:
创建队列;
将起点插入队列中;
while(队列不为空)
获取队列元素个数;
轮数+1;
while(当未完成上一轮加入到队列中节点的遍历)
取出队头元素;
更新起点当当前点的距离(轮数)
上一轮元素个数-1;
遍历与当前元素相连的节点,将其插入队列中;但是,当图为有权图时,BFS不再适用,此时Dijkstra算法应运而生,其具体的思想是创建两个集合,其中第一个集合S即为源点到其他节点的距离,另一个集合V则是为在前一个集合中的节点。初始时S中有且只有源点,然后遍历集合V,找到距离源点最近的节点,将该节点从V中取出放入S中,然后以该节点为源节点,重复以上步骤即可。伪代码如下:
创建距离数组dist
将所有节点放入一个未访问集合中(notfound)
将起点到自身的距离初始化为0
for i = 1:n (进行n-1轮循环,即不用确定到自身的距离)
遍历notfound集合以找到其中的最小值
用上述最小值更新对应的距离
将该最小值对应的节点从notfound中取出
用最小值更新notfound数组 Dijkstra算法虽然巧妙,但是不能应对边权值出现负数的情况,此时就需要用到Bellman_Ford或者SPFA算法,后面会再提及。Dijkstra实际上是用来解决单源点最短路径问题,而要解决多源点问题则需要对源点逐一调用Dijkstra算法,而Floyd则是用来解决多源点问题。其思路非常简单。首先创建一个距离数组记为dist[][],其中dist[i][j]表示节点i到节点j的最短距离。通过图,选择中间节点(遍历),然后以i到中间节点再到节点j的距离去更新dist[i][j]即可。伪代码如下:
直接使用邻接矩阵
遍历中间节点:
遍历起点i:
遍历终点j:
dist[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k]+dp[k][j]);对于负权值图或者有中间节点数限制的情况,Dijkstra难以处理,而Bellman_ford算法则可以很好的解决这个问题,但是同样是解决单源点最短路径问题。具体实现就是创建一个距离数组dist,初始化源点到自身的距离,然后遍历整个图n-1次(即从源点到某个点的最短距离可能为n-1条边的情况).
代码实现
- 朴素Dijkstra算法
/*
@param:
edges: 采用邻接矩阵的形式
src: 源点
n: 节点数
@return:
源点src到其他点的最短距离
*/
vector<int> dijkstra(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int src) {
vector<int> dist(n, -1), notfound(n, INT_MAX);
// 初始化未访问列表
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
notfound[i] = edges[src][i];
}
dist[src] = 0;
notfound[src] = -1;
// dijkstra核心代码
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int minval = INT_MAX, minindex;
// 找notfound中的最小值
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(notfound[j] != -1 && notfound[j] < minval) {
minval = notfound[j];
minindex = j;
}
}
dist[minindex] = minval;
notfound[minindex] = -1; // 表示该点已经访问过了
// 以找到的最小点为源点,更新notfound集合
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
// 在未访问集合中且由minindex节点到当前点是可达的
if(dist[j] == -1 && edges[minindex][j] > 0) {
int newdistance = edges[minindex][j] + minval;
// 之前j节点不可达,或到达j节点路径比当前路径长
if(notfound[j] == -1 || notfound[j] > newdistance) {
notfound[j] = newdistance;
}
}
}
}
return dist;
}- 堆优化Dijkstra算法
/*
@param:
edges: 采用邻接矩阵/邻接表的形式,下面的代码采用邻接矩阵的方式
src: 源点
n: 节点数
@return:
源点src到其他点的最短距离
*/
#define pii pair<int,int>
vector<int> dijkstra(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int src) {
vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX/2);
dist[src] = 0;
priority_queue<pii, vector<pii>, greater<pii> > pq;
pq.emplace(0, src);
while(!pq.empty()) {
auto [curcost, curid] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if(edges[curid][i] > 0) {
int newcost = curcost + edges[curid][i];
if(dist[i] > newcost) {
pq.emplace(newcost, i);
dist[i] = newcost;
}
}
}
}
return dist;
}- Floyd算法
/*
@param:
edges: 采用邻接矩阵的形式
@return:
返回各个节点到其他节点的最短距离
*/
vector<vector<int>> floyd(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> dist(edges);
for(int k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k], dist[k][j]);
}
}
}
return dist;
}- Bellman_ford算法
/*
@param:
edges: 采用边的形式
n: 节点个数
src: 源点
@return:
源点src到其他点的最短距离
*/
vector<int> bellman_ford(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int n, int src) {
vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX/2);
dist[src] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for(auto edge: edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
dist[v] = min(dist[v], dist[u]+w);
}
}
} 相关习题
题目链接:1091. 二进制矩阵中的最短路径
给你一个
n x n的二进制矩阵grid中,返回矩阵中最短 畅通路径 的长度。如果不存在这样的路径,返回-1。二进制矩阵中的 畅通路径 是一条从 左上角 单元格(即,
(0, 0))到 右下角 单元格(即,(n - 1, n - 1))的路径,该路径同时满足下述要求:路径途经的所有单元格都的值都是
0。
路径中所有相邻的单元格应当在 8 个方向之一 上连通(即,相邻两单元之间彼此不同且共享一条边或者一个角)。
畅通路径的长度 是该路径途经的单元格总数。示例1:
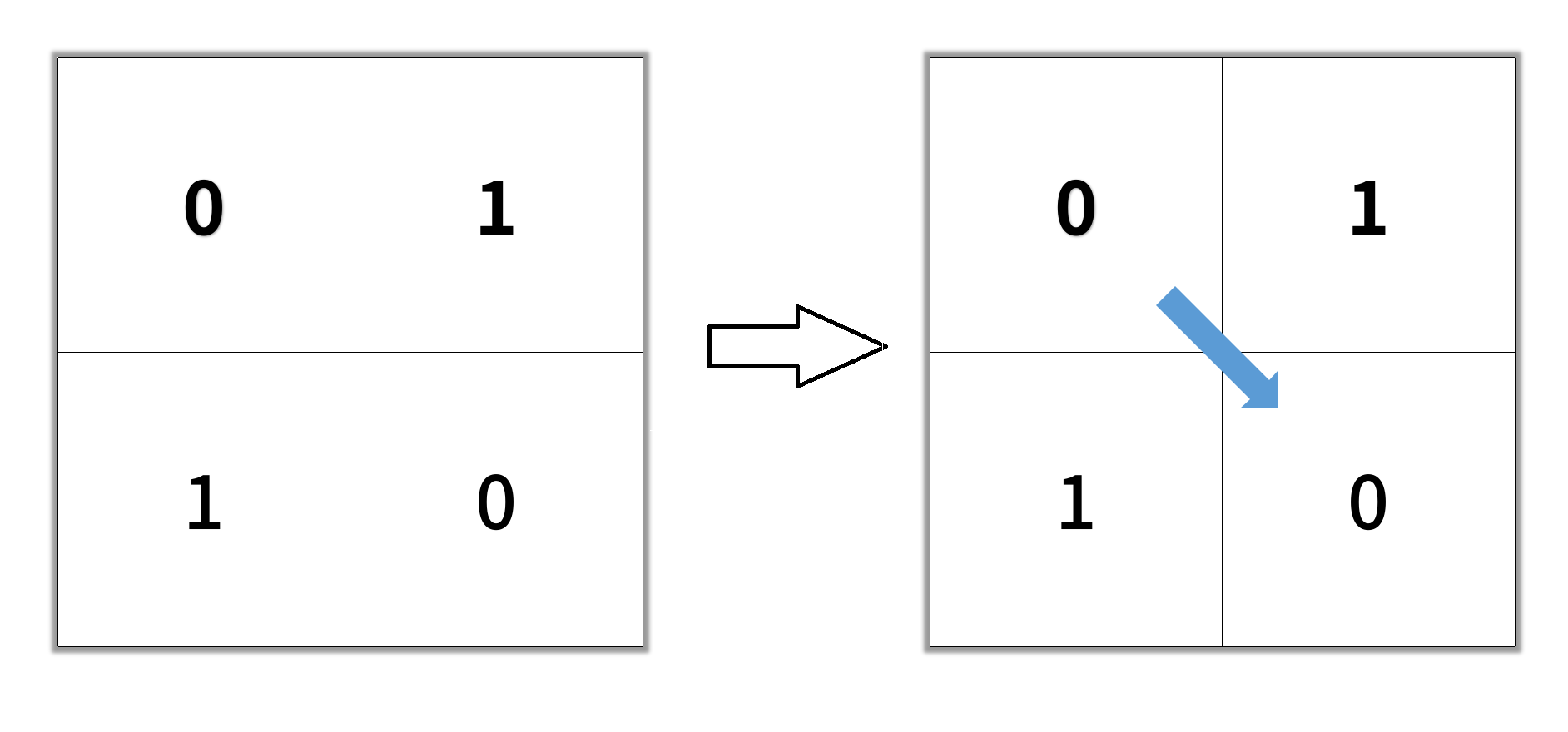
输入: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]]
输出: 2示例2:
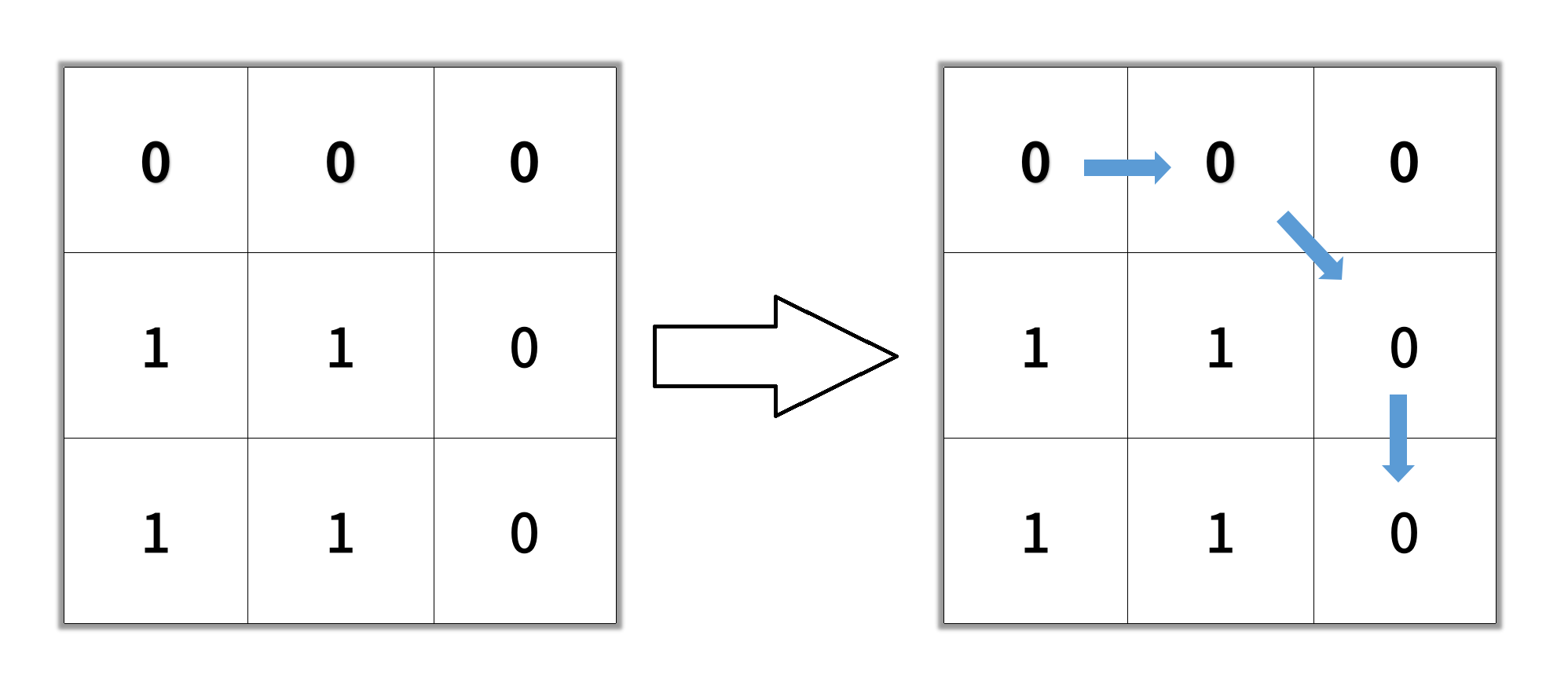
输入: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
输出: 4示例3:
输入: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
输出: -1- 思路:无权无向图的单源点最短路径问题,直接BFS即可。
- 代码:
class Solution { int dir[8][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1 ,1, 1, 1}; public: int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int n = grid.size(); queue<pair<int, int>> q; if(grid[0][0]==1 || grid[n-1][n-1]==1) return -1; int res = 1; q.emplace(0, 0); grid[0][0] = 1; while(!q.empty()) { int size = q.size(); while(size--) { auto [curx, cury] = q.front(); q.pop(); if(curx == n-1 && cury == n-1) return res; for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) { int newx = curx + dir[i][0], newy = cury + dir[i][1]; if(newx < 0 || newx >= n || newy < 0 || newy >= n) { continue; }else if(grid[newx][newy] == 1) { continue; } grid[newx][newy] = 1; q.emplace(newx, newy); } } ++res; } return -1; } }; - 类似的题目:题目链接:1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口
题目链接:542. 01 矩阵
给定一个由
0和1组成的矩阵mat,请输出一个大小相同的矩阵,其中每一个格子是mat中对应位置元素到最近的0的距离。两个相邻元素间的距离为
1。示例1:
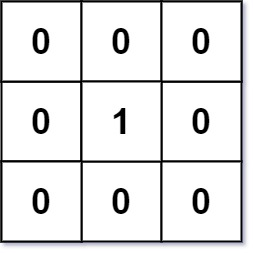
输入: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
输出: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]示例2:
输入: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
输出: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]- 思路:多源点最短路径问题,直接用BFS即可,先将所有的零放入队列中,然后遍历,当遇到1就更新对应方格的距离(原值与当前BFS的轮数中的较小值)。
- 代码:
class Solution { int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0}; public: vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int n = mat.size(), m = mat[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> ret(n, vector<int>(m, INT_MAX)); queue<pair<int, int>> q; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < m; ++j) { if(mat[i][j] == 0) { ret[i][j] = 0; q.emplace(i, j); } } } while(!q.empty()) { auto [curx, cury] = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newx = curx+dir[i][0], newy = cury+dir[i][1]; if(newx<0||newx>=n||newy<0||newy>=m) continue; if(ret[newx][newy] > ret[curx][cury]+1) { q.emplace(newx, newy); ret[newx][newy] = ret[curx][cury]+1; } } } return ret; } };
题目链接:743. 网络延迟时间
有
n个网络节点,标记为1到n。给你一个列表
times,表示信号经过 有向 边的传递时间。times[i] = (ui, vi, wi),其中ui是源节点,vi是目标节点,wi是一个信号从源节点传递到目标节点的时间。现在,从某个节点
K发出一个信号。需要多久才能使所有节点都收到信号?如果不能使所有节点收到信号,返回-1。示例1:
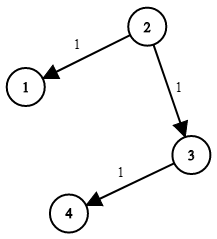
输入: times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2
输出: 2示例2:
输入: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1
输出: 1示例3:
输入: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2
输出: -1- 思路:有向有权图求源点到其他节点的最短路径的最大值,实际上直接用Dijkstra求路径长度,然后遍历找最大值即可。
代码:
class Solution { struct Node { int nextid; int cost; Node(int id, int _cost): nextid(id), cost(_cost) {} bool operator<(const Node node) const { return cost > node.cost; } }; vector<vector<Node>> edges; public: int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int k) { edges = vector<vector<Node>> (n+1); vector<int> dis(n+1, -1); for(auto vec: times) { int from = vec[0], to = vec[1], cost = vec[2]; edges[from].emplace_back(to, cost); } priority_queue<Node> pq; pq.emplace(k, 0); dis[k] = 0; while(!pq.empty()) { auto [curid, curcost] = pq.top(); pq.pop(); for(auto [nextid, nextcost]: edges[curid]) { if(dis[nextid] == -1 || dis[nextid] > curcost+nextcost) { dis[nextid] = curcost+nextcost; pq.emplace(nextid, dis[nextid]); } } } int ret = INT_MIN; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if(dis[i] == -1) return -1; ret = max(ret, dis[i]); } return ret; } };类似的题目:
题目链接:787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
有
n个城市通过一些航班连接。给你一个数组flights,其中flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei],表示该航班都从城市fromi开始,以价格pricei抵达toi。现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市
src和目的地dst,你的任务是找到出一条最多经过k站中转的路线,使得从src到dst的 价格最便宜 ,并返回该价格。 如果不存在这样的路线,则输出-1。示例1:
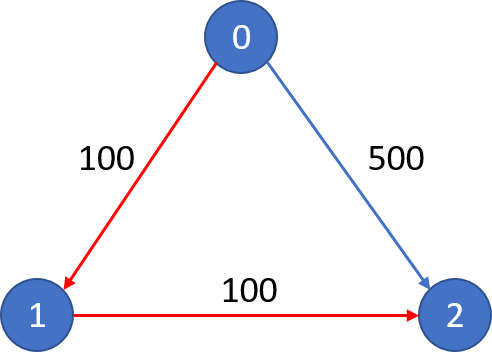
输入: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]]
src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
输出: 200示例2:
输入: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]]
src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
输出: 500- 思路:有向有权图求源点到目标节点的花费最小且中间节点不超过限制的路径,与上一题不同的是,这一题多了一个中间节点次数的限制。那么直接通过Dijkstra可能就无法得到正确的答案,即最优的方案中间节点可能超过限制,次优的次数不超过限制,此时次优应该是答案而不是最优方案,而Bellman_Ford则正好可以解决次数限制的问题,只需要将外层的迭代次数设置为限制次数即可。Bellman_Ford算法的外层迭代次数实际上就是确保节点到其他任意节点的路径都走过一次,即由源点到其他点所经过的节点数至多为n-1个,而当将次数修改为限制次数时,此时就是至多经过k个节点了。
- 代码:
class Solution { public: int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) { vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX/2); dist[src] = 0; for(int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) { vector<int> tmpdist(dist); for(auto& vec: flights) { int from = vec[0], to = vec[1], cost = vec[2]; dist[to] = min({dist[to], tmpdist[to], tmpdist[from]+cost}); } } return dist[dst] == INT_MAX/2 ? -1 : dist[dst]; } };
题目链接:1334. 阈值距离内邻居最少的城市
有
n个城市,按从0到n-1编号。给你一个边数组edges,其中edges[i] = [fromi, toi, weighti]代表fromi和toi两个城市之间的双向加权边,距离阈值是一个整数distanceThreshold。返回能通过某些路径到达其他城市数目最少、且路径距离 最大 为
distanceThreshold的城市。如果有多个这样的城市,则返回编号最大的城市。注意,连接城市
i和j的路径的距离等于沿该路径的所有边的权重之和。示例1:
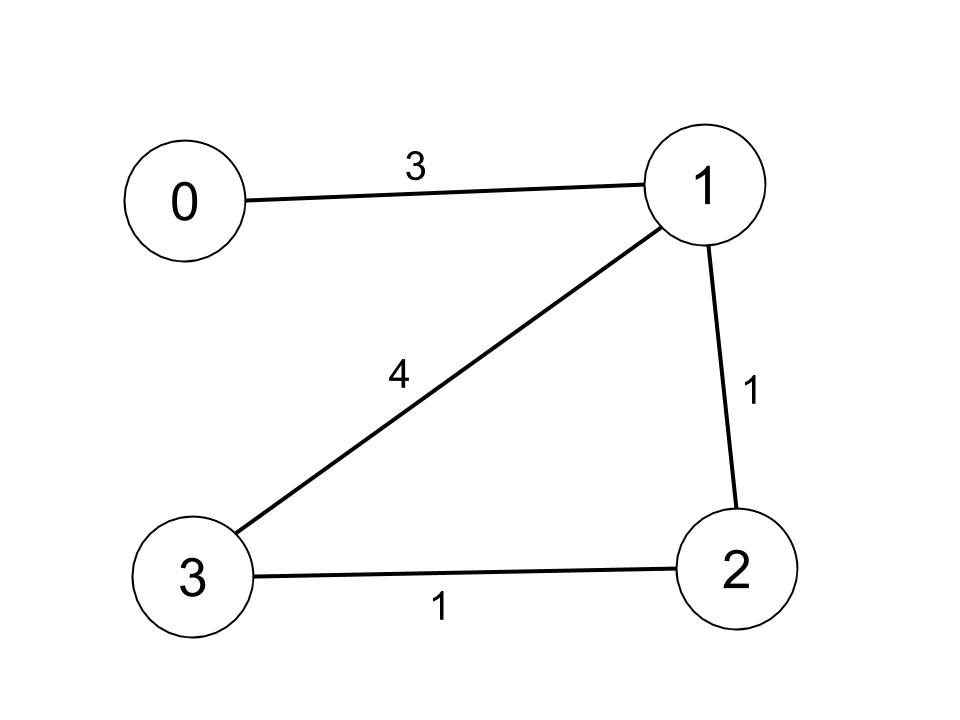
输入: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[1,2,1],[1,3,4],[2,3,1]], distanceThreshold = 4
输出: 3示例2:
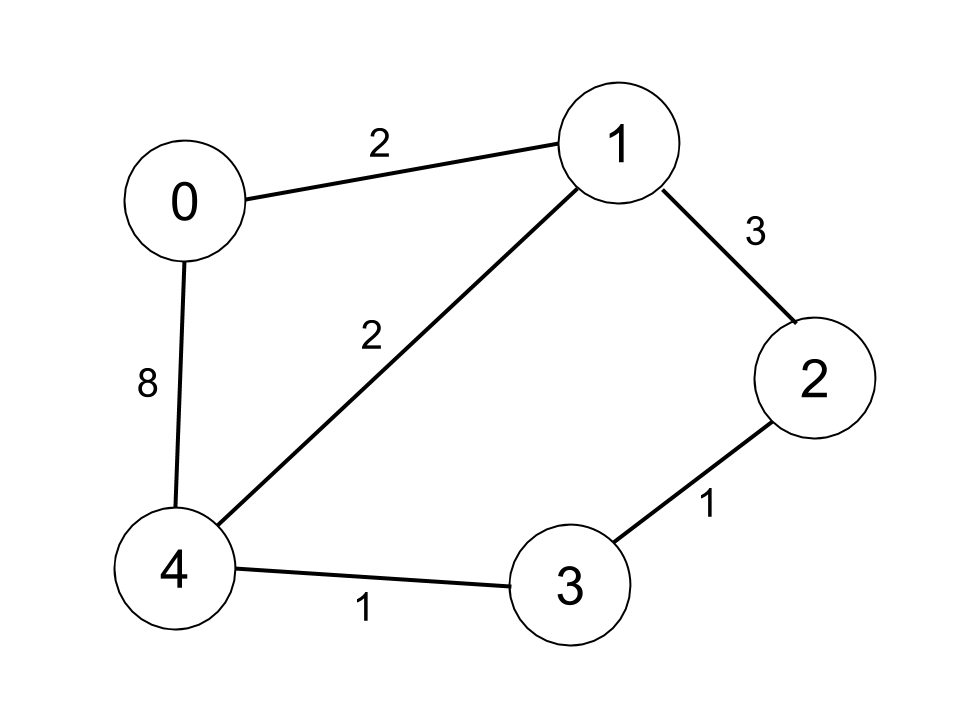
输入: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,4,8],[1,2,3],[1,4,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], distanceThreshold = 2
输出: 0- 思路:求无向有权图中每个节点到其他节点的最短距离,然后计算每个节点到其他节点的距离小于阈值的个数,找到个数最少且编号最大的那个节点。实际上就是多源点最短路径问题,可以采用Dijkstra迭代实现,也可以通过Bellman_Ford迭代实现,更直接的是采用Floyd算法来完成,当距离矩阵求完后,遍历矩阵求节点距离小于阈值个数然后更新答案即可。
- 代码:
class Solution { public: int findTheCity(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int distanceThreshold) { vector<vector<int>> dist(n, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX/2)); // 初始化距离矩阵 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) dist[i][i] = 0; for(auto edge: edges) { int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2]; dist[u][v] = dist[v][u] = w; } // Floyd核心 for(int k = 0; k < n; ++k) { for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k]+dist[k][j]); } } } // 求节点距离小于阈值的节点数最少的最大节点编号 int mincnt = INT_MAX, minindex; for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int cnt = 0; for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { if(i == j) continue; if(dist[i][j] <= distanceThreshold) ++cnt; } if(mincnt >= cnt) { mincnt = cnt; minindex = i; } } return minindex; } }; - 类似的题目:1462. 课程表 IV
华子9.7机考t2
地图大小为M*N,其中地图为X表示无法通过,为B表示可以通过,S为起点,E为终点,求起点到终点的最小耗费,注意,改变方向时需要额外花费1.- 思路:单源点无向有权图(转方向权值变为2)最短路径问题,Dijkstra,加上个方向变量即可。
- 代码:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> using std::cin; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::priority_queue; using std::vector; enum DIR {NONE=0, LEFT, RIGHT, UP, DOWN}; int direction[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0}; int M, N; struct edge { int row; int col; int cost; DIR dir; edge(int r, int c, int _cost, DIR _dir): row(r), col(c), cost(_cost), dir(_dir){} bool operator<(const edge& node) const { return cost > node.cost; } }; DIR getdir(int i) { // 获取方向 switch(i){ case(0): return RIGHT; case(1): return DOWN; case(2): return LEFT; case(3): return UP; default: return NONE; } } int solution(vector<vector<char>>& map, int sx, int sy, int ex, int ey) { priority_queue<edge> pq; pq.emplace(sx, sy, 0, NONE); vector<vector<int>> dist(M, vector<int>(N, INT_MAX/2)); dist[sx][sy] = 0; while(!pq.empty()) { auto cur = pq.top(); pq.pop(); int curr = cur.row, curc = cur.col, curcost = cur.cost; if(curr == ex && curc == ey) return curcost; DIR curdir = cur.dir; for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newr = curr + direction[i][0], newc = curc + direction[i][1]; if(newr < 0 || newr >= M || newc < 0 || newc >= N) continue; // 越界 else if(map[newr][newc] == 'X') continue; // 不可通过 int newcost = curcost + 1; if(curdir != NONE && getdir(i) != curdir) ++newcost; // 修改方向 if(newcost < dist[newr][newc]) { dist[newr][newc] = newcost; pq.emplace(newr, newc, newcost, getdir(i)); } } } return -1; } int main(void) { while(cin >> M >> N) { int sx, sy, ex, ey; vector<vector<char>> map(M, vector<char> (N)); for(int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { cin >> map[i][j]; if(map[i][j] == 'S') sx = i, sy = j; // 保存起点坐标 else if(map[i][j] == 'E') ex = i, ey = j; // 保存终点坐标 } } cout << solution(map, sx, sy, ex, ey) << endl; } return 0; }
华子9.7机考t3
给定M*N大小的地图,为0表示通道(可通过,不可停车),为1/2表示该格为停车位(1表示空车位,2表示车位已停了车),其他不用管。给定停车场入口坐标,求起点到最近的闲置空位的路径。- 思路:单源点无权无向图,Dijkstra即可解决,区别是要找到整个路径,那么需要用一个哈希表来保存当前点以及上一个点的映射,即当前点从哪个点来的,最后遍历到终点时,以当前点为索引从哈希表中取出上一个点,然后用上一个点从哈希表中取出上上个点…最后把路径旋转一下即可。
代码:
int direction[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0}; int N, M; struct Node { int row; int col; int cost; Node(int r, int c, int _cost): row(r), col(c), cost(_cost){} bool operator<(const Node& node) const { return cost > node.cost; } }; vector<vector<int>> solution(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int> entrance) { vector<vector<int>> ret; priority_queue<Node> pq; map<pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>> hash; pq.emplace(entrance[0], entrance[1], 0); vector<vector<int>> dist(M, vector<int>(N, INT_MAX/2)); dist[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = 0; while(!pq.empty()) { auto cur = pq.top(); pq.pop(); int curr = cur.row, curc = cur.col, curcost = cur.cost; if(curr-1>=0 && edges[curr-1][curc] == 1) { ret.push_back({curr-1, curc}); pair<int, int> tmp = make_pair(curr, curc); while(hash[tmp] != tmp) { ret.push_back({tmp.first, tmp.second}); tmp = hash[tmp]; } reverse(ret.begin(), ret.end()); return ret; } else if(curr+1<M && edges[curr+1][curc] == 1) { ret.push_back({curr+1, curc}); pair<int, int> tmp = make_pair(curr, curc); while(hash[tmp] != tmp) { ret.push_back({tmp.first, tmp.second}); tmp = hash[tmp]; } reverse(ret.begin(), ret.end()); return ret; } for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newr = curr + direction[i][0], newc = curc + direction[i][1]; if(newr<0 || newr>=M || newc<0 || newc>=N) continue; else if(edges[newr][newc] != 0) continue; int newcost = curcost + 1; if(newcost >= dist[newr][newc]) continue; hash.insert({{newr, newc}, {curr, curc}}); dist[newr][newc] = newcost; pq.emplace(newr, newc, newcost); } } return {{-1, -1}}; } int main(void) { while(cin >> M >> N) { vector<int> entrance(2); cin >> entrance[0] >> entrance[1]; --entrance[0]; --entrance[1]; vector<vector<int>> edges(M, vector<int>(N)); for(int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { cin >> edges[i][j]; } } vector<vector<int>> res = solution(edges, entrance); for(auto vec: res) { cout << vec[0]+1 << " " << vec[1]+1 << " "; } cout << endl; } return 0; }华子9.21笔试t2
给定M*N的棋盘,起点为(0, 0), 终点为(M-1, N-1), 士每次只能走一格,马可以走“日”字(不会被阻挡),棋盘上为X的格子表示无法到达,为S表示棋子状态可以进行修改(马转士或士转马,但花费会+1).- 思路:类似9.7的t2,原本是单源无权无向图,增加了可以修改状态后变为单源无向有权图,所以采用Dijkstra算法,并加设两个状态矩阵,表示某个格子上是否已经出现过某个状态以进行剪枝。
- 代码:
int N, M; int dir1[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0}; // 士 int dir2[8][2] = {1, 2, 2, 1, 2, -1, -1, 2, -1, -2, -2, -1, -2, 1, 1, -2}; // 马 enum STATE {SOL=0, HOR}; // 士/马 struct Node { int row; int col; int cost; STATE st; Node(int r, int c, int _cost, STATE _st): row(r), col(c), cost(_cost), st(_st){} bool operator<(const Node& node) const { return cost > node.cost; } }; int solution(vector<vector<char>>& map) { priority_queue<Node> pq; vector<vector<bool>> horse(M, vector<bool>(N, false)), soldier(M, vector<bool>(N, false)); if(map[0][0] == 'S') { pq.emplace(0, 0, 0, SOL); pq.emplace(0, 0, 1, HOR); }else if(map[0][0] == '.') { pq.emplace(0, 0, 0, SOL); }else { return -1; } while(!pq.empty()) { auto cur = pq.top(); pq.pop(); int curr = cur.row, curc = cur.col, curcost = cur.cost, curst = cur.st; if((curst == HOR && horse[curr][curc]) || (curst == SOL && soldier[curr][curc])) continue; if(curr == M-1 && curc == N-1) return curcost; if(curst == SOL) { soldier[curr][curc] = true; for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { int newr = curr + dir1[i][0], newc = curc + dir1[i][1]; if(newr<0 || newr>=M || newc<0 || newc>=N) continue; else if(map[newr][newc] == 'X') continue; pq.emplace(newr, newc, curcost+1, SOL); if(map[newr][newc] == 'S') pq.emplace(newr, newc, curcost+2, HOR); } }else { horse[curr][curc] = true; for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) { int newr = curr + dir2[i][0], newc = curc + dir2[i][1]; if(newr<0 || newr>=M || newc<0 || newc>=N) continue; else if(map[newr][newc] == 'X') continue; pq.emplace(newr, newc, curcost+1, HOR); if(map[newr][newc] == 'S') pq.emplace(newr, newc, curcost+2, SOL); } } } return -1; } int main(void) { while(cin >> M >> N) { vector<vector<char>> map(M, vector<char>(N)); for(int i = 0; i < M; ++i) { for(int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { cin >> map[i][j]; } } cout << solution(map) << endl; } return 0; }
存图方式
邻接矩阵:密集图时采用,其余情况不考虑,否则对于稀疏图来说,如果节点数过大,遍历整个图将需要$n^2$的时间,从而导致超时
邻接表:对于稀疏图,常采用该方法,一般定义为
vector<vector<int>> edge(n);,其中n为节点数字典:即通过哈希表来存储图,通常定义为
unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, int>> edge;,分别存储边的两个端点以及对应的边权。链式前向星:通过静态数组实现链表,调用add方法向图中添加对应的边。
const int maxn = 10001; struct { int to; int next; int cost; }edges[maxn]; int head[maxn]; int cnt; void init(void) { for(int i = 0; i < maxn; ++i) head[i] = -1; cnt = 0; } // 添加一条u->v的边权为w的有向边,当图为无向图时需要调用两次添加两条相反的边 // 因而maxn应该大于边数的两倍 void add(int u, int v, int w) { edges[cnt].to = v; edges[cnt].next = head[u]; edges[cnt].w = w; head[u] = cnt++; } // 遍历方法 /* cout << "from: " << i << endl; for(int j = head[i]; j != -1; j = edge[j].next) { cout << "to: " << edge[j].to << endl; cout << "cost: " << edge[j].cost << endl; } */

